In terms of odds ratios, we can say that for male students, the odds ratio is exp (13) = 114 for a oneunit increase in math score and the odds ratio for female students is exp (197) = 122 for a oneunit increase in math score Figure2 Odds as a fraction Odds should NOT be confused with Probabilities Odds are the ratio of something happening to something not happeningIn our scenario above, the odds are 4 to 6 Whereas, Probability is the ratio of something happening to everything that could happenSo in the case of our chess example, probability is 4 to 10 (as there were 10 games In mathematics, the term odds can be defined as the ratio of number of favourable events to the number of unfavourable events While odds for an event indicates the probability that the event will occur, whereas odds against will reflect the likelihood of nonoccurrence of the event
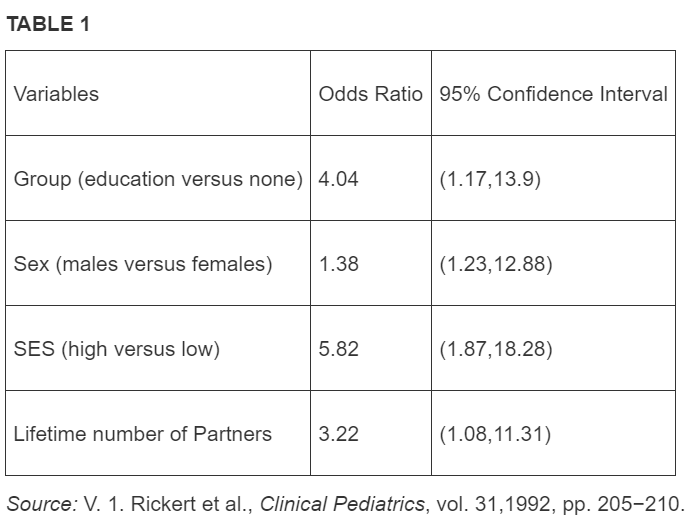
Solved Table1 Variables Odds Ratio 95 Confidence Interva Chegg Com
Risk difference vs odds ratio
Risk difference vs odds ratio- Odds ratio An odds ratio (OR) is another measure of association that quantifies the relationship between an exposure with two categories and health outcome Referring to the four cells in Table 315, the odds ratio is calculated as Odds ratio = ( The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring program




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download
The odds aren't as odd as you might think, and the log of the odds is even simpler! Smoking The adjusted odds ratio for smoking is calculated as e485 = 1624 This means the odds of having a baby with low birthweight are increased by 624% if the mother smokes (compared to not smoking), assuming the variable age is held constant For example, suppose mother A and mother B are both 30 years oldThe odds ratio is a way of comparing whether the odds of a certain outcome is the same for two different groups (9) The odds ratio is simply the ratio between the following two ratios The ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who died, and the ratio between standard treatment and the new drug for those who survived
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a 12 paper"Odds" and "Risk" are the most common terms which are used as measures of association between variables In this article, which is the fourth in the series of common pitfalls in statistical analysis, we explain the meaning of risk and odds and the difference between the twoThe 95% confidence interval for this odds ratio is between 333 and 593
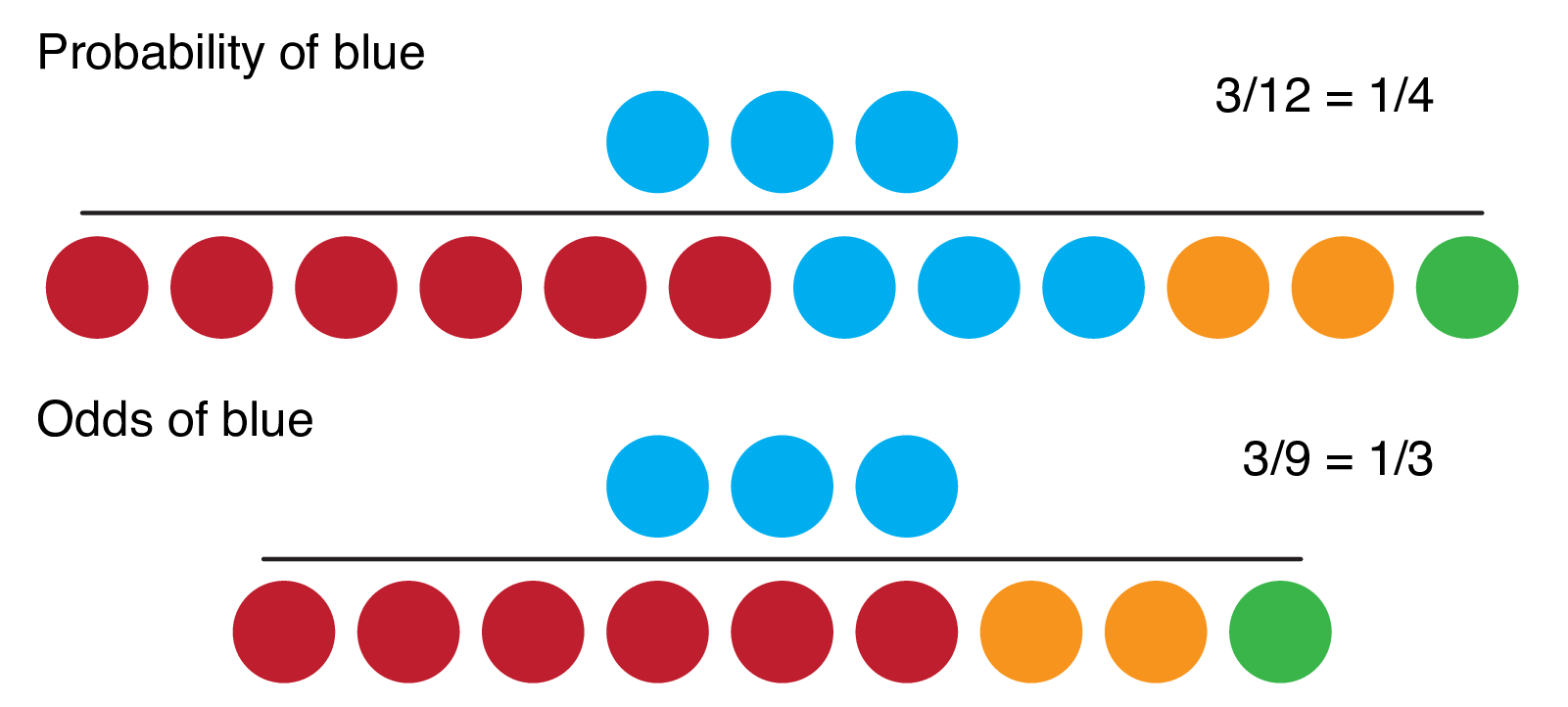
The difference between cats and dogs is 3 percentage points or 3 49 ≈ 612 % increase in probability for dogs over cats Meanwhile the odds ratio is 052 1 − 052 049 1 − 049 ≈ 1128 However I am finding a lot of social science literature intpreting O R − 1 as equivalent to increase in probability Example Odds seems less intuitive It is the ratio of the probability a thing will happen over the probability it won't In the spades example, the probability of drawing a spade is 025 The probability of not drawing a spade is 1 025This is called the odds ratio;




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
Fractional odds are sometimes called British odds or traditional odds and are sometimes written as a fraction, such as 6/1, or expressed as a ratio, like sixtoone Decimal odds represents theDecimal odds represent the amount one wins for every $1 wagered An odds ratio is a relative measure of effect, which allows the comparison of the intervention group of a study relative to the comparison or placebo group So when researchers calculate an odds ratio they do it like this The numerator is the odds in the intervention arm The denominator is the odds in the control or placebo arm = Odds Ratio (OR)



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss



1
Express odds numerically Generally, odds are expressed as the ratio of favorable outcomes to unfavorable outcomes, often using a colon In our example, our odds of success would be 2 4 two chances that we'll win versus four chances that we'll lose Like a fraction, this can be simplified to 1 2 by dividing both terms by the common multiple of 2 An Odds Ratio (OR) then is simply the comparison of two odds, OR=Odds (A)/Odds (B) The Relative Risk (RR) is simply the comparison of two risks or probabilities, RR=Probability (A)/Probability (B) This is made more clear when the term is referred to as the Risk Ratio Let's look at this graphicallyRELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
The odds ratio (OR) is a measure of how strongly an event is associated with exposure The odds ratio is a ratio of two sets of odds the odds of the event occurring in an exposed group versus the odds of the event occurring in a nonexposed group Odds ratios commonly are used to report casecontrol studies Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated Risk vs odds The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different implications and are calculated in different ways Odds is a concept that is very familiar to gamblers It is a ratio of probability that a particular event will occur and can be any number between zero and infinity




Solved Table1 Variables Odds Ratio 95 Confidence Interva Chegg Com




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
This brings us to today's topic Odds Ratio (OR) vs Relative Risk (RR) Odds vs Probability why we love them and why these two cousin statistics continue to confuse us Anyone with a math, science, or medical background has been taught this, and ifAs an extreme example of the difference between risk ratio and odds ratio, if action A carries a risk of a negative outcome of 999% while action B has a risk of 990% the relative risk is approximately 1 while the odds ratio between A and B is 10 (1% = 01% x 10), more than 10 times higherOdds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatment




Acsh Explains Odds And Odds Ratios American Council On Science And Health




Crude Odds Ratios Cor And Adjusted Odds Ratio Aor And Their 95 Download Table
An example of what I am talking about is the choice between risk ratio and odds ratio Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokersIt is called that because it is the ratio of two odds Some people call the odds the odds ratio because the odds itself is a ratio That is fine English, but this can quickly lead to confusion If you did that, you would have to call this calculation the odds ratio ratio or the ratio of the odds ratios The difference between odds ratio and risk ratio While Risk Ratio is the probability of one thing divided by the probability of another (usually in a separated group), Odds Ratio is the odds of one event happening divided by the odds of another EssoeOdds1




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
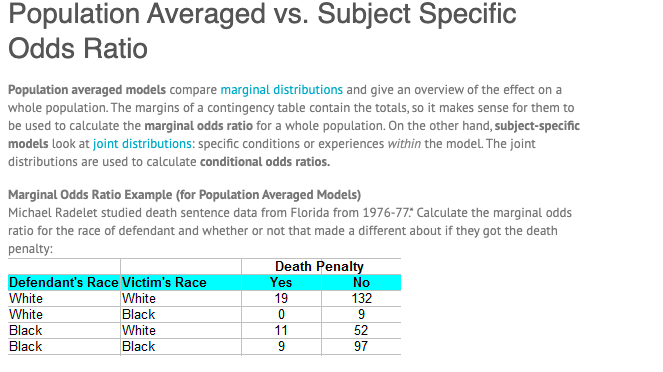



Population Averaged Vs Subject Specific Odds Ratio Chegg Com
Odds Ratios and Log(Odds Ratios) are like RSquared they describe a relationship between two things And just like RSquared, you need to determine if this The odds ratio comparing the new treatment to the old treatment is then simply the correspond ratio of odds (01/09) / (02/08) = 0111 / 025 = 0444 (recurring) This means that the odds of a bad outcome if a patient takes the new treatment are 0444 that of the odds of a bad outcome if they take the existing treatment The odds ratio is extremely important, however, as it is the only measure of effect that can be computed in a casecontrol study design When the outcome of interest is relatively rare (




Statquest Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction
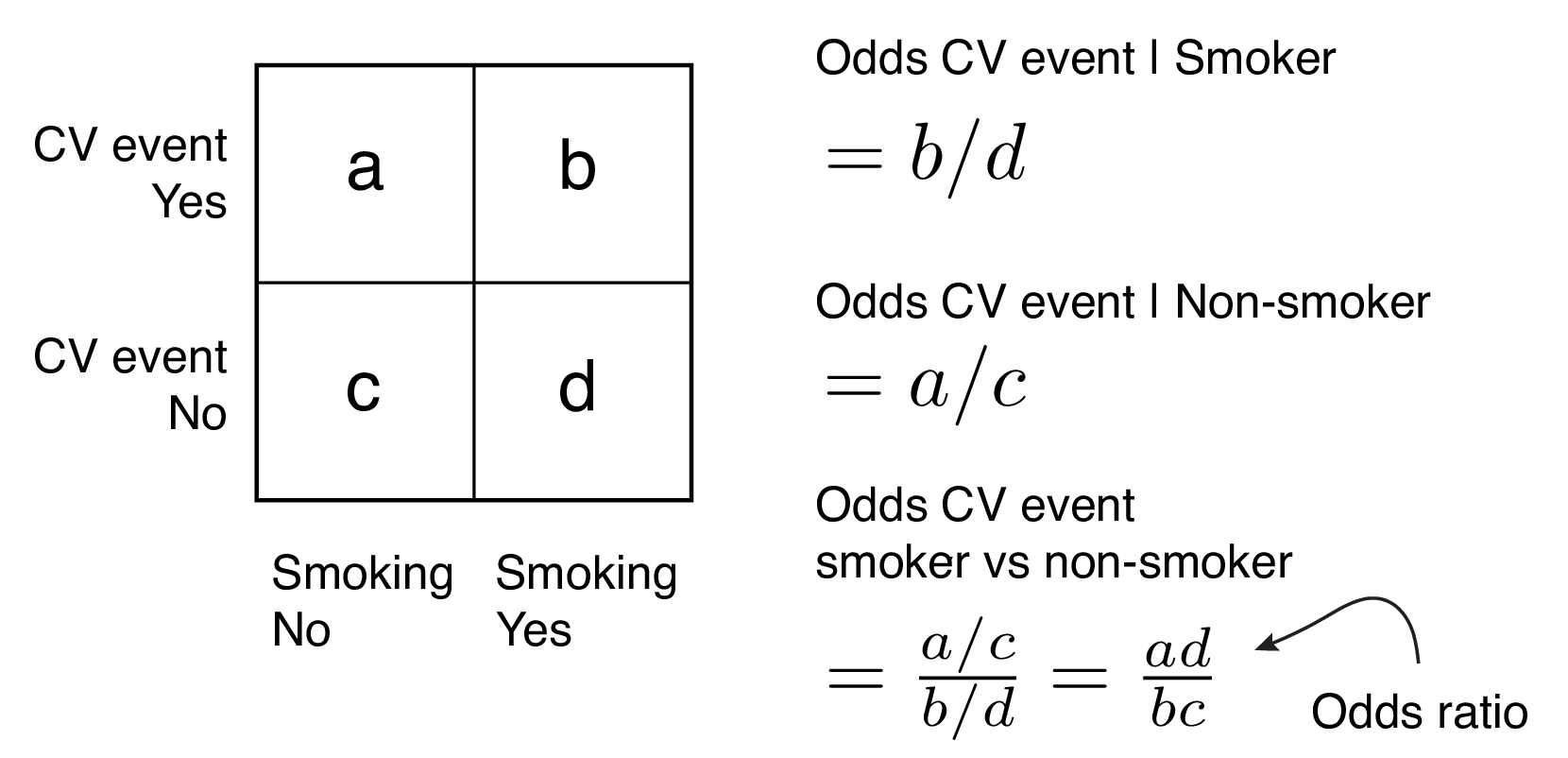
This StatQuest covers those subjects so that you can understand the stati The process of calculating probabilities from odds can be generalised by the following equation, where H is a certain hypothesis and O(H) are the odds in favour of that hypothesis (the ratio of the bet of winning vs losing) OR (a/c)/ (b/d) = ad∗cb The risk, or probability, and the odds are related with the following formula risk = Odds 1 odds from which we can infer that if the risk or the probability of failure is low ( P




Idiot S Guide To Odds Ratios Journalfeed




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
The odds ratio for picking a red ball compared to a green ball is calculated as Odds (red) / Odds (green) = 4 / 025 = 16 Thus, the odds of picking a red ball are 16 times larger than the odds of picking a green ball When Are Odds Ratios Used in the Real World?In video two we review / introduce the concepts of basic probability, odds, and the odds ratio and then apply them to a quick logistic regression example UnOdds and Odds Ratios Odds are the probability of an event happening / the probability of an event not happening Thus the odds of throwing a three with one die is 1/5 odds = probability / (1 probability) and conversely probability = odds / (1 odds) Odds Ratio Odds ratio is the ratio of odds for the exposed group vs the unexposed group




Odds Ratio Article
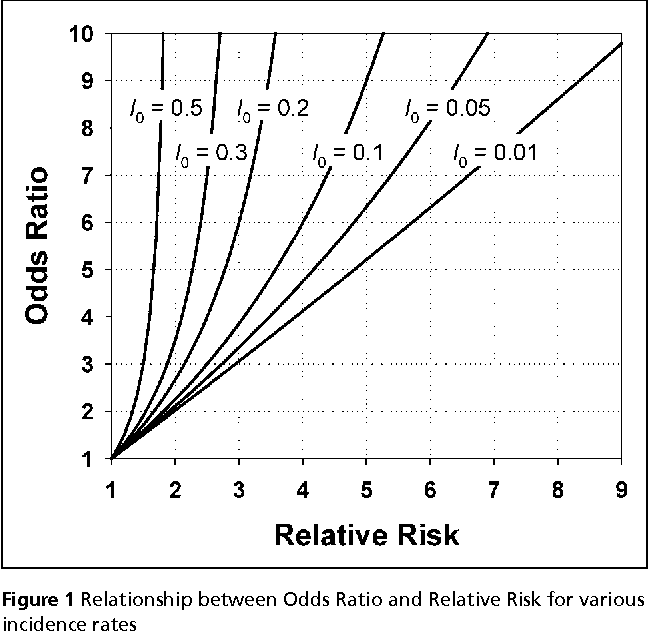



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar
The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio is from 10, the more likely it is that the relationship between the exposure and the disease is causal For example, an odds ratio of 12 is above 10, but is not a strong association An odds ratio of 10 suggests a stronger association Odds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of XOdds ratio is the likelihood that an event will occur in relation to the likelihood that an event will not occur, 1 event for and 5 events against In Gambling, the "odds" are a ratio of the likelihood of a certain outcome, related to the other outcomes I had to look this up, because I forgot this part of finite math, from 25 years ago




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To
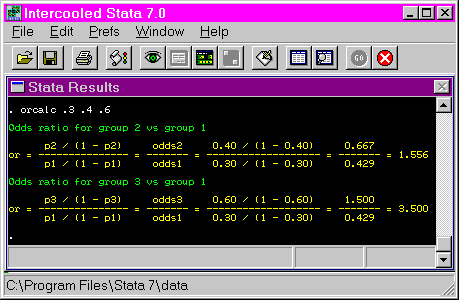



Stata Teaching Tools Odds Ratio Calculation
Odds are defined as the ratio of the probability of success and the probability of failure The odds of success are odds (success) = p/ (1p) or p/q =8/2 = 4, that is, the odds of success are 4 to 1• Probability is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, while Odds is expressed as a ratio • Probability ensures that an event will occur, but Odds is used to find out whether the event will ever occurAn odds ratio greater than 1 indicates that the condition or event is more likely to occur in the first group And an odds ratio less than 1 indicates that the condition or event is less likely to occur in the first group The odds ratio must be nonnegative if it is defined




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk



The Difference Between Probability And Odds
The Rcode above demonstrates that the exponetiated beta coefficient of a logistic regression is the same as the odds ratio and thus can be interpreted as the change of the odds ratio when we increase the predictor variable \(x\) by one unit In this example the odds ratioThe odds ratio of lung cancer for smokers compared with nonsmokers can be calculated as (647*27)/(2*622) = 1404, ie, the odds of lung cancer in smokers is estimated to be 14 times the odds of lung cancer in nonsmokers We would like to know how reliable this estimate is?Fractional odds are the ratio of the amount (profit) won to the stake;




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy
Definition The Odds Ratio is a measure of association which compares the odds of disease of those exposed to the odds of disease those unexposed Formulae OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in the nonexposed) Example I often think food poisoning is a good scenario to consider when interpretting ORs Imagine a group of friends went out to e x p (β) = odds ratio = p 1 1 − p 1 p 2 1 − p 2 I guess what's not coming across is how β, not being a ratio of odds, converts to the odds ratio metric, when taken out of logarithmic space To provide a bit more, if this is the logistic regression equation for the constant Nonlinear measures like the odds ratio do not have an obvious causal interpretation when applied to individuals From a Neyman/Rubin causal model perspective, a simple and appropriate measure is simply the difference in proportions, which is the population average of the causal effect for an individual, the difference in the outcome (1 or 0




Plot Of Power Versus Odds Ratios Using 700 Controls Initial Analysis Download Scientific Diagram




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube
What is the difference between Probability and Odds? Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk When two groups are under study or observation, you can use two measures to describe the comparative likelihood of an event happening These two measures are the odds ratio and relative risk Both are two different statistical concepts, although so much related to each other Simply put, an odds ratio of 5 (ie 5 times greater likelihood) shows a much stronger association than odds ratio of 3, which in turn is stronger than an odds ratio of 15 Lastly, the odds ratio tells us the direction of the association between the factor and the outcome




Cohort Specific And Meta Analysis Pooled Odds Ratios Ors Of Download Scientific Diagram



Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar
Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4



Statquest Odds And Log Odds Clearly Explained Youtube




Figure 7 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Younger And Older Subgroups Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For
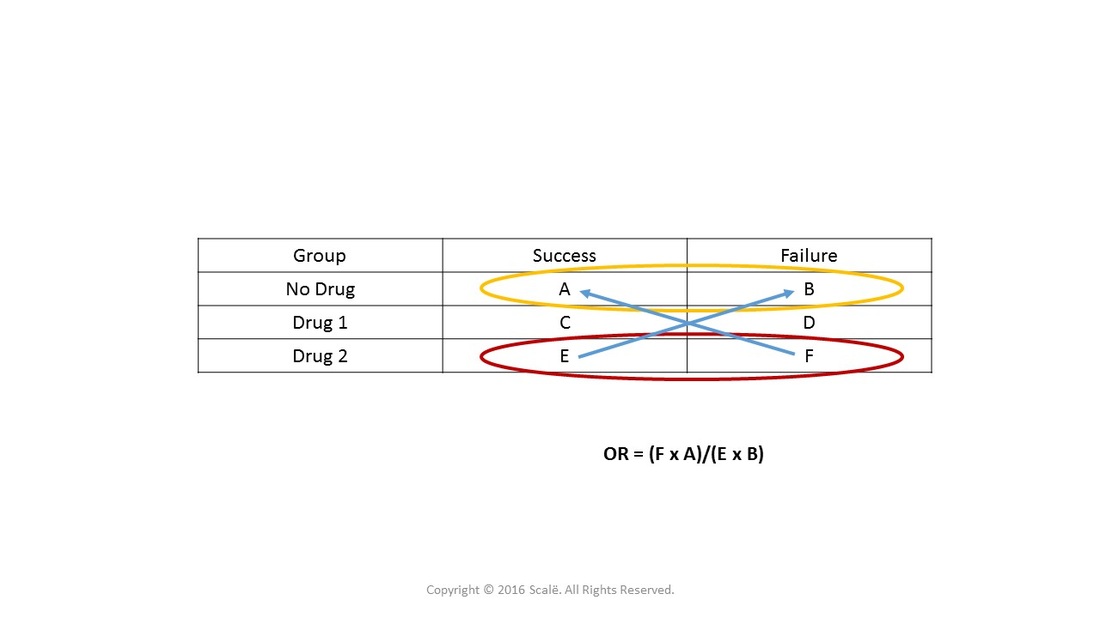



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss




Plotting Odds Ratio Vs Continuous Variable In Stata Stack Overflow
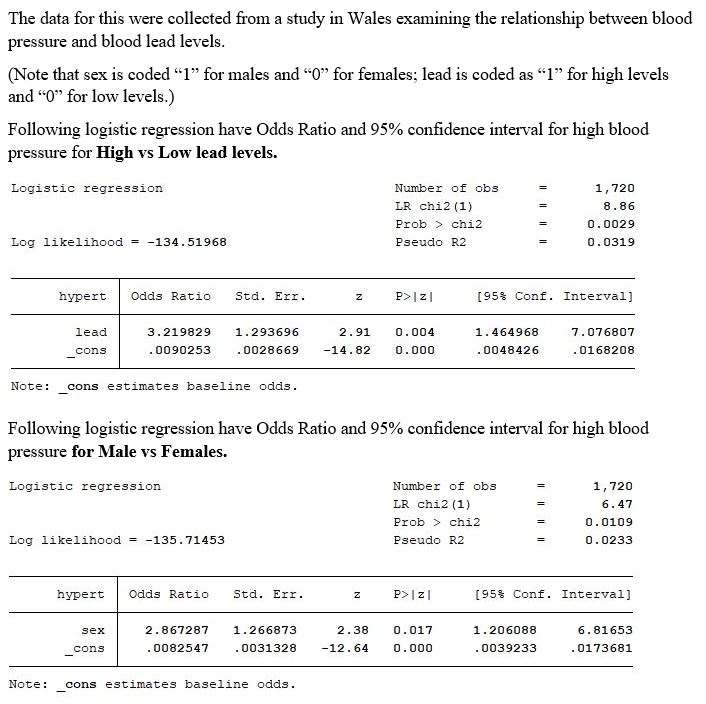



1 Based On The Information Provided Above Interpret Chegg Com




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Risk Ratio Versus Odds Ratio Dr Journal Club




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk




Odds Ratio Vs Risk Ratio Exercise The Odds Ratio Chegg Com
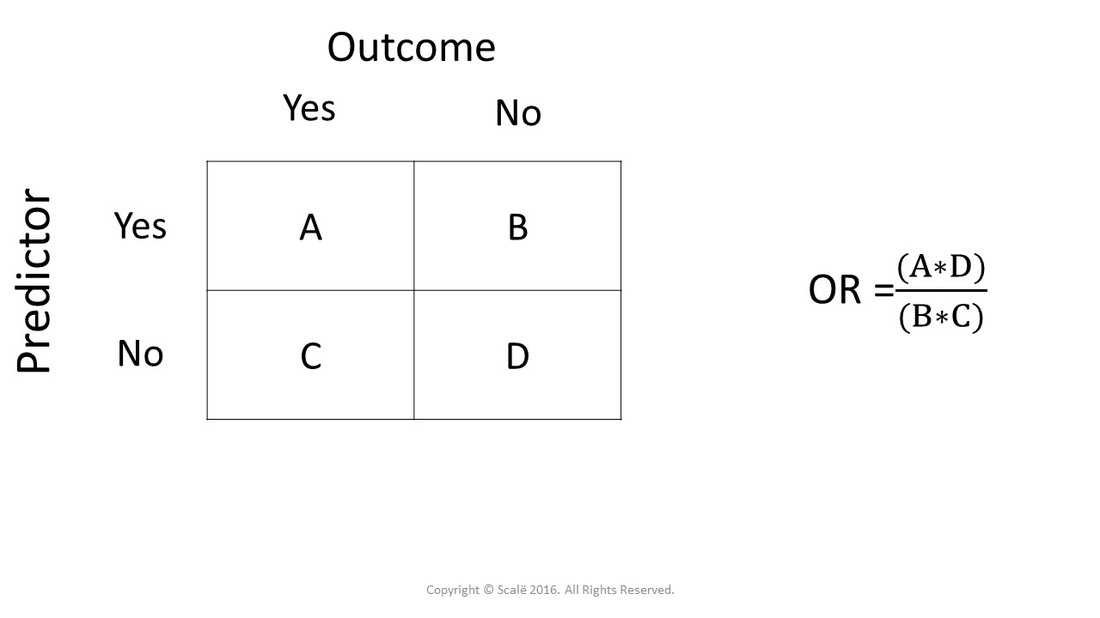



Calculate Odds Ratio With 95 Confidence Intervals
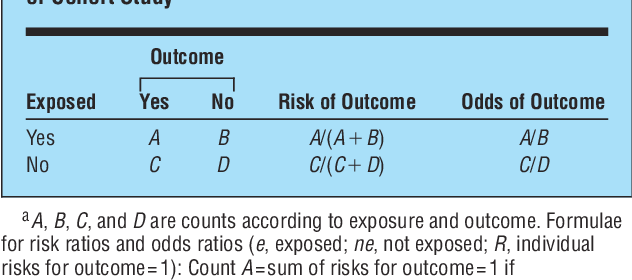



Table 1 From The Relative Merits Of Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science



1




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube




Moving Beyond Odds Ratios Estimating And Presenting Absolute




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science



Risk Ratio Vs Odds Ratio Hunter 19 Notes And Things




Figure 99 Pooled Odds Ratios Of Gastrointestinal Adverse Events And Strength Of Evidence For Monotherapy And Metformin Based Combination Comparisons Diabetes Medications For Adults With Type 2 Diabetes An Update Ncbi Bookshelf



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss



Idiot S Guide To Odds Ratios Journalfeed




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




One Odds Ratio For More Vs Less Employment Odds Ratios Are For A 1 Download Scientific Diagram




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Extensive Video Youtube



Q Tbn And9gcq5tpzikqe8jiy9iqzxyqcbaqndofe8d2iabvvrkarpadvgvm8o Usqp Cau



Logit Of Logistic Regression Understanding The Fundamentals By Saptashwa Bhattacharyya Towards Data Science




The Odds Ratios Ors Mean Difference Md With 95 Confidence Download Scientific Diagram




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Odds Ratio Wikipedia
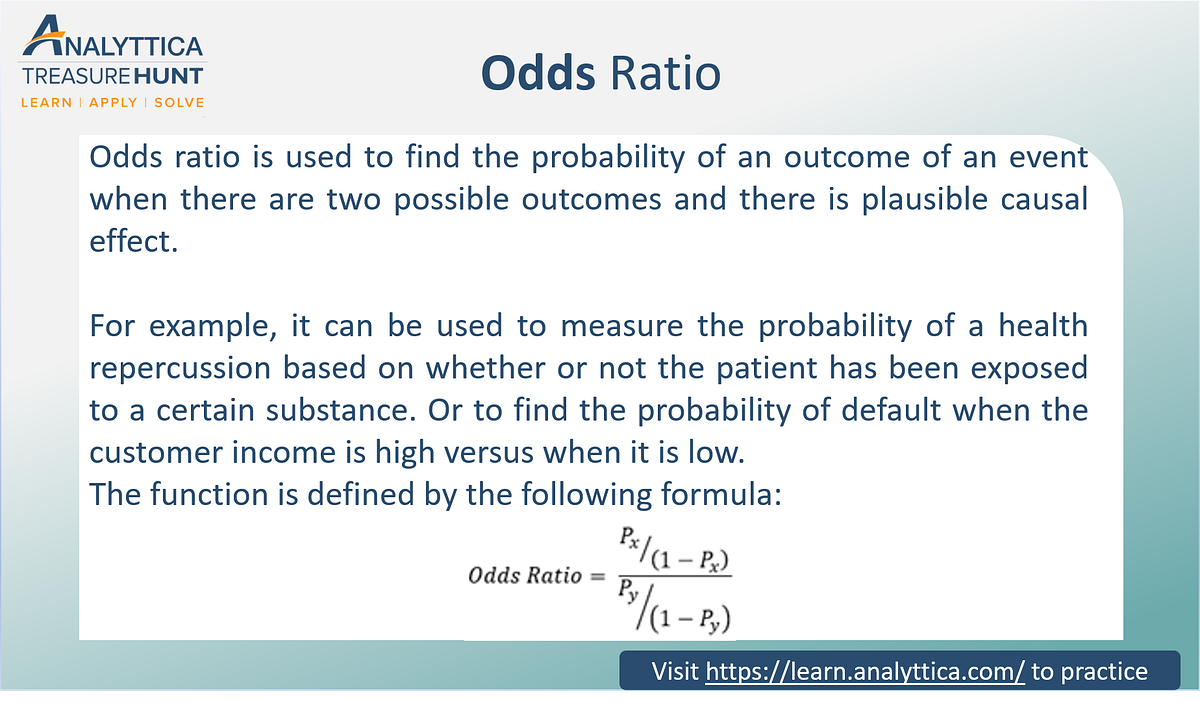



Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium




Funnel Plots Comparing Log Odds Ratio Or Versus The Standard Error Of Download Scientific Diagram
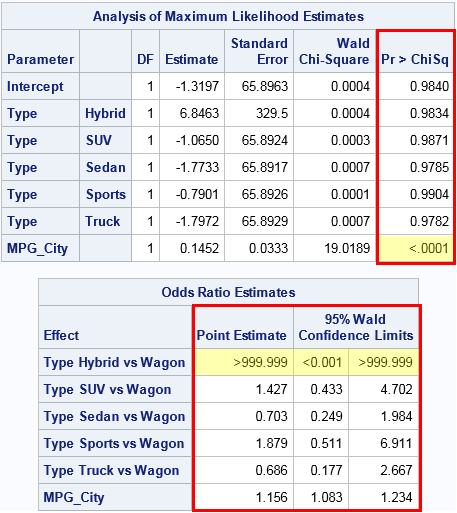



Formats For P Values And Odds Ratios In Sas The Do Loop




Volcano Plot From Univariate Analysis Depicting Odds Ratio Versus Download Scientific Diagram



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




How To Calculate Odds Ratio Learn What Odds Ratio Means




Crude And Adjusted Odds Ratio Or Of Adverse Birth And Infant Outcomes Download Table



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios
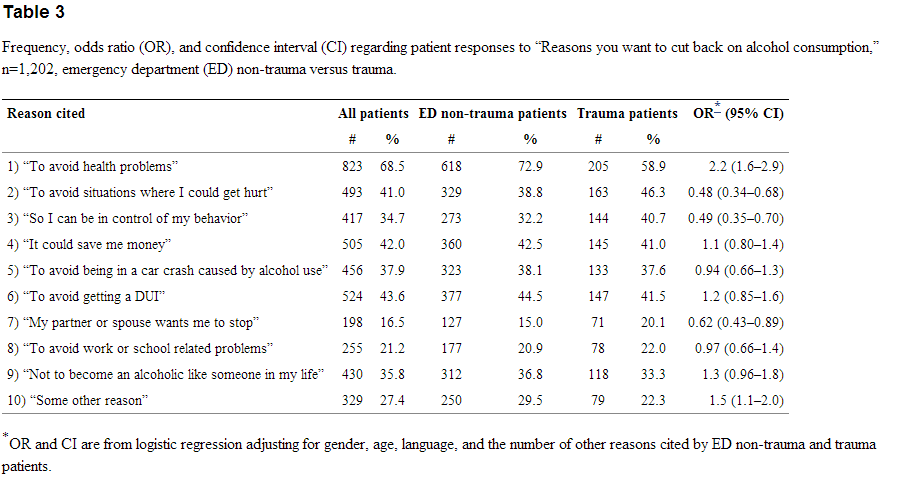



Table 3 Frequency Odds Ratio Or And Confidence Interval Ci Regarding Patient Responses To Reasons You Want To Cut Back On Alcohol Consumption N 1 2 Emergency Department Ed Non Trauma Versus Trauma The




Odds Ratios For Highest Versus Lowest Quartile Download Table




What Is A Pooled Odds Ratio Quora
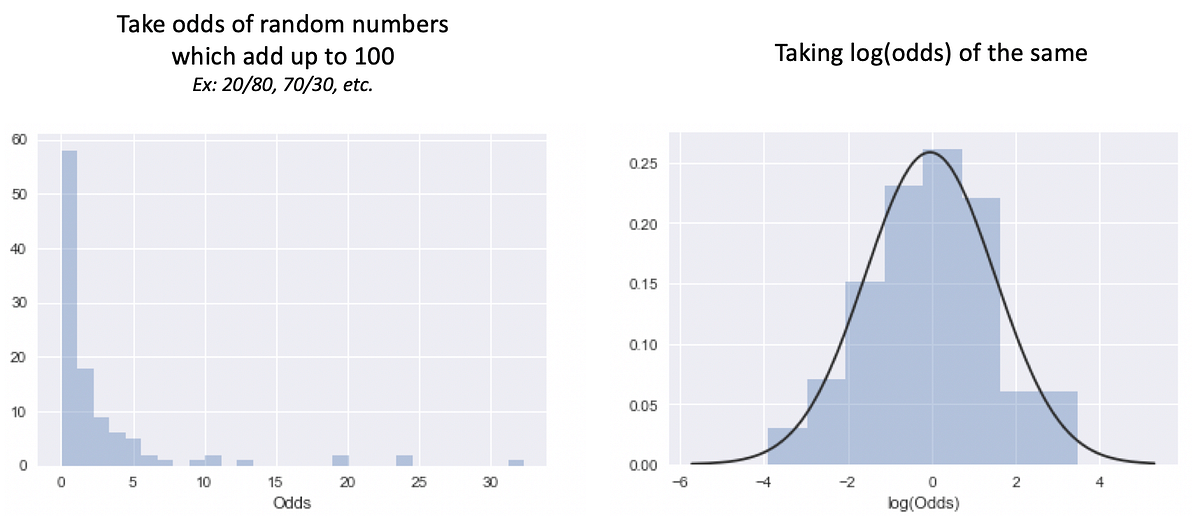



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Adjusted Odds Ratios Of Hospitalizations With Cannabis Use Disorder Download Table
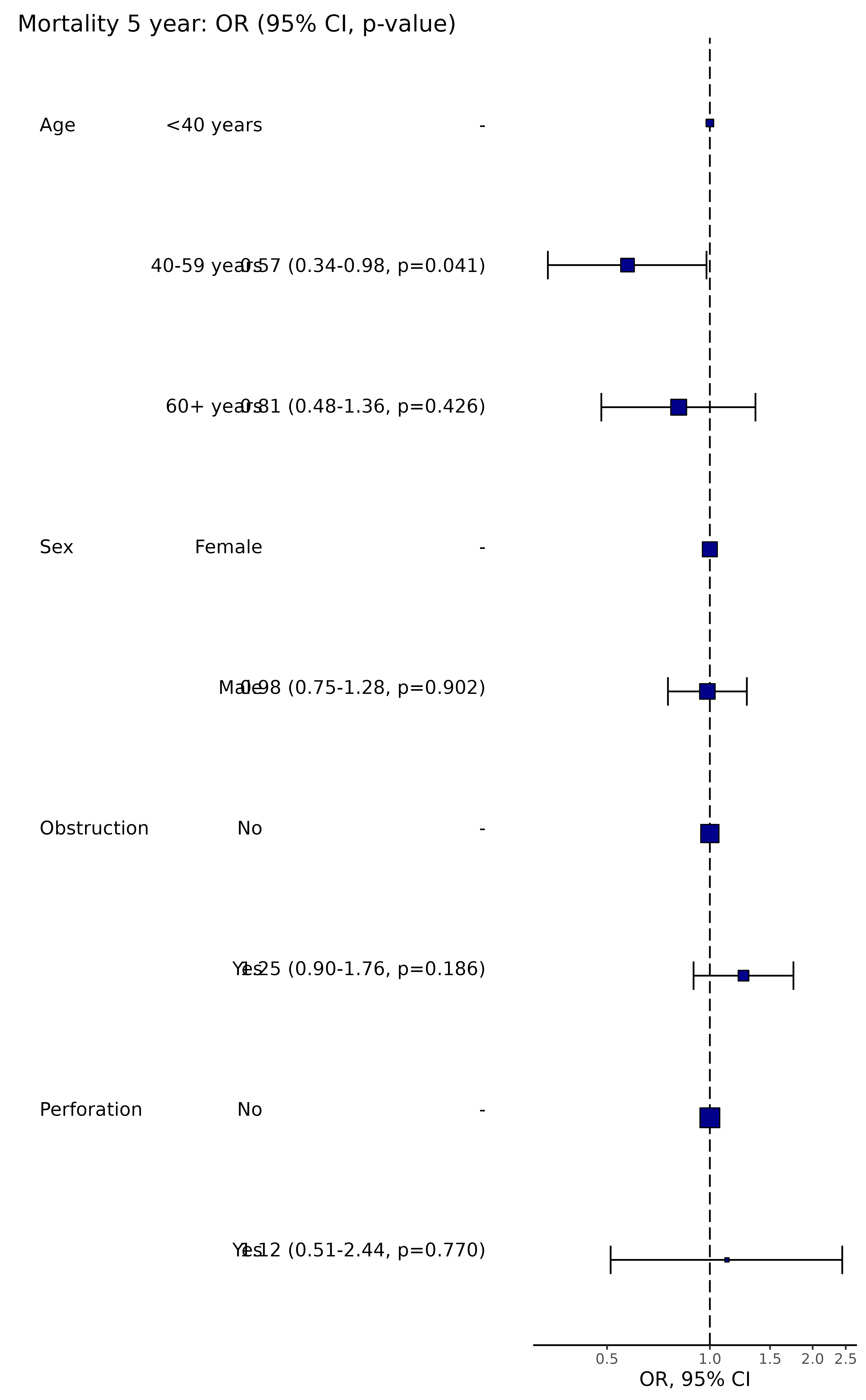



Produce An Odds Ratio Table And Plot Or Plot Finalfit




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




File Odds Ratio Relatives Risiko Jpg Wikimedia Commons
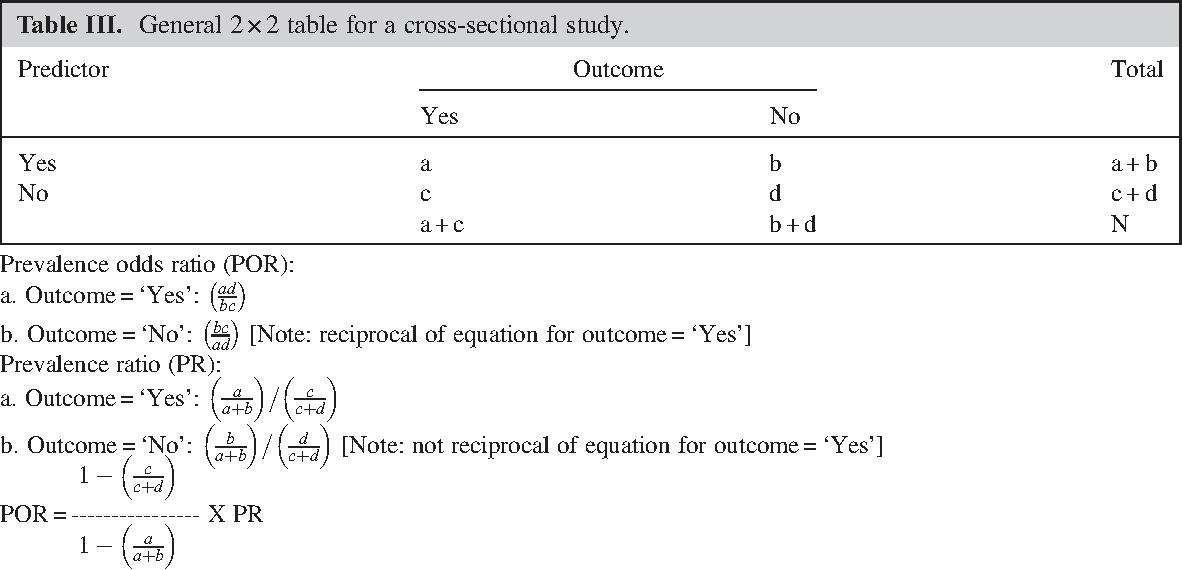



Pdf Prevalence Odds Ratio Versus Prevalence Ratio Choice Comes With Consequences Semantic Scholar



Odds Ratio Calculation




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February




Graph Of Odds Ratio Versus Sleep Image Eurekalert Science News




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy
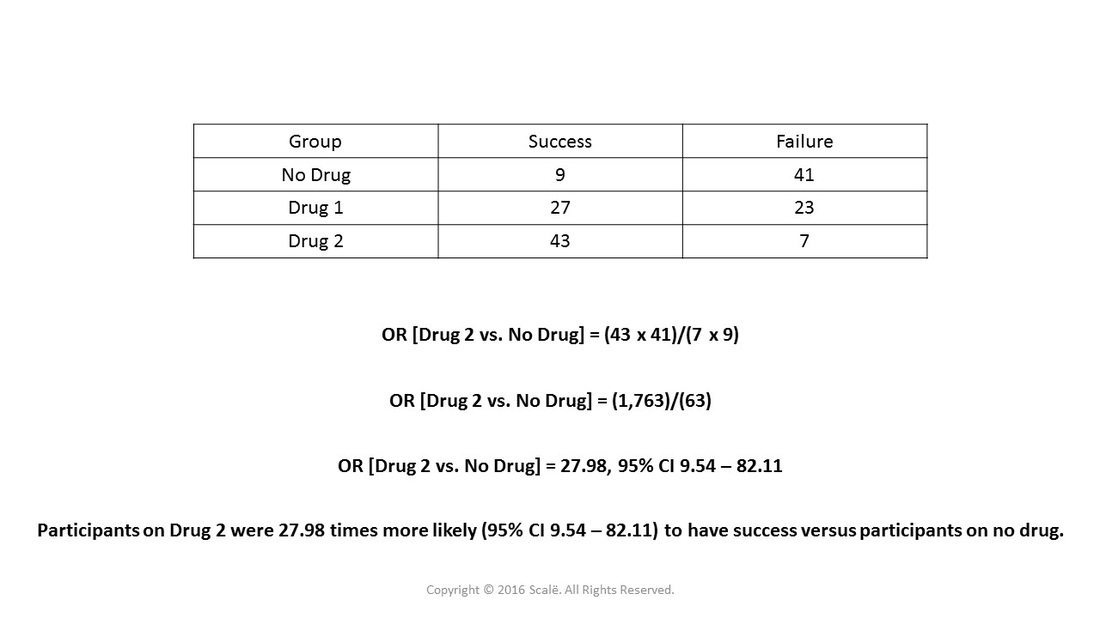



Use And Interpret Unadjusted Odds Ratio In Spss
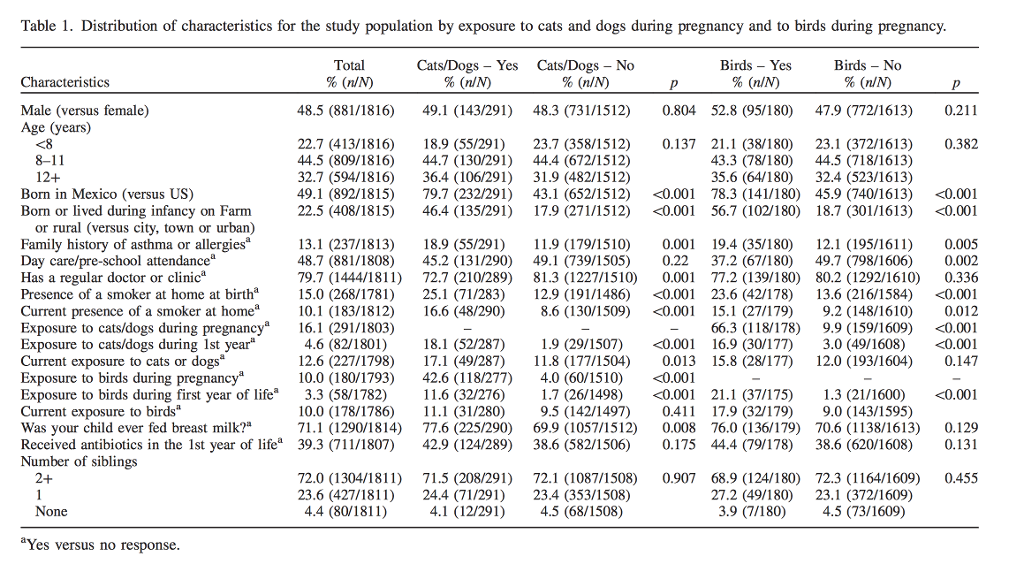



Calculating Odds Ratio Using Table 1 Calculate Chegg Com




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Odds Or Probability Sense About Science Usa
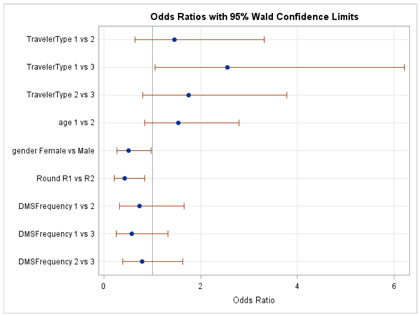



Public Perception Of Safety Messages And Public Service Announcements On Dynamic Message Signs In Rural Areas Appendix C Odds Ratio Graphs For Evaluation Of Hypotheses




Figure 6 Random Effects Model Meta Analysis Of Relative Odds Ratio Of Icd Vs No Icd For Arrhythmic Death Between Women And Men Assessment On Implantable Defibrillators And The Evidence For Primary




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿